The CSR segment will contain fundamental administrative and regulatory information required to document a patient's enrollment on a clinical trial. This segment is all that is required if one needs to message another system that an enrollment has taken place, i.e., from clinical trials to pharmacy, accounting, or order entry systems. The CSR segment may also be used to identify that OBR, OBX, RXA, and RXR segments that follow represent data applicable to the identified study.
| Seq# | DataElement | Description | Must Implement | Flags | Cardinality | Length | C.LEN | Vocabulary | DataType |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||||||
 1
1
|
01011 | Sponsor Study ID | SHALL | [1..1] | EI | ||||
 2
2
|
01036 | Alternate Study ID | [0..1] | EI | |||||
 3
3
|
01037 | Institution Registering the Patient | [0..1] | CWE | |||||
 4
4
|
01038 | Sponsor Patient ID | SHALL | [1..1] | CX | ||||
 5
5
|
01039 | Alternate Patient ID - CSR | [0..1] | CX | |||||
 6
6
|
01040 | Date/Time of Patient Study Registration | SHALL | [1..1] | DTM | ||||
 7
7
|
01041 | Person Performing Study Registration | [0..*] | XCN | |||||
 8
8
|
01042 | Study Authorizing Provider | SHALL | [1..*] | XCN | ||||
 9
9
|
01043 | Date/Time Patient Study Consent Signed |
MAY
 True:
True:
 False:
False:
|
C |
[1..1] [0..1] |
DTM | |||
 10
10
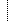
|
01044 | Patient Study Eligibility Status |
MAY
 True:
True:
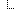 False:
False:
|
C |
[1..1] [0..1] |
CWE | |||
 11
11
|
01045 | Study Randomization Date/time | [0..3] | DTM | |||||
 12
12
|
01046 | Randomized Study Arm | [0..3] | CWE | |||||
 13
13
|
01047 | Stratum for Study Randomization | [0..3] | CWE | |||||
 14
14
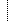
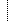
|
01048 | Patient Evaluability Status |
MAY
 True:
True:
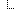 False:
False:
|
C |
[1..1] [0..1] |
CWE | |||
 15
15
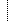
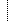
|
01049 | Date/Time Ended Study |
MAY
 True:
True:
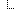 False:
False:
|
C |
[1..1] [0..1] |
DTM | |||
 16
16
|
01050 | Reason Ended Study |
MAY
 True:
True:
 False:
False:
|
C |
[1..1] [0..1] |
CWE | |||
 17
17
|
00816 | Action Code | [0..1] | [2..2] | ID | ||||
(Definition from CSR.1 in Ch. 7)
Definition: The field contains the universal identifier for the clinical trial. Since many clinical trials are collaborative and multi-centered, and since one goal of these standards is to promote automated data exchange among sites, the primary identifier should come from the sponsor. The coding system component may reference the sponsor. Example:
T93-0807^NCI (where NCI refers to the National Cancer Institute).
(Definition from CTI.1 in Ch. 7)
Definition: This field contains the universal identifier for the clinical trial. The coding system is as described in CSR-1 Sponsor Study ID.
(Definition from CM0.2 in Ch. 8)
Definition: This field contains the study number established by the study sponsor. Please see discussion in Chapter 7, section 7.7.1.1, "Sponsor study ID."
(Definition from CSR.2 in Ch. 7)
Definition: This field contains an alternate identifier that may be used as agreed upon by messaging parties. For example, the sending application may code its internal study number here.
(Definition from CM0.3 in Ch. 8)
Definition: This field contains the local or collaborators' cross-referenced study numbers.
Definition: This field distinguishes the institution where registration occurred. The legal approval to give patients access to a trial lies with the Internal Review Board for the institution. Universal healthcare provider facility codes should be used when they exist. Currently coding systems must be devised by users. Refer to Table 0589 - Institution Registering the Patient in Chapter 2C for valid values.
Definition: This field contains the main patient identification for the study. The sponsor patient ID allows automation of records on patients treated at various institutions. The sponsor patient ID should be unique for each patient participating on the study identified in CSR-1 Sponsor Study ID.
Definition: This field may be the sending application's patient identification. Coding conventions may be used as agreed upon by users.
Definition: This field containing the date of the patient registration is mandatory. The time component is optional. The time stamp for a registration may be useful. For example, patients may be randomized at the pharmacy according to the order in which they were registered.
Definition: This field contains the healthcare facility employee who actually phoned, submitted a form, or interactively registered the patient on the clinical trial. This is generally done under authorization from the attending physician or a principal or collaborating investigator.
Definition: This field contains the healthcare provider, generally the attending physician, who is accountable that the patient is eligible for the trial and has signed an informed consent. National standard healthcare provider codes should be used when they exist. This field is required for the patient registration trigger event (C01).
Definition: This field contains the consent form signing date is collected to provide a checkpoint that the consent form was obtained. Since many trials involve unapproved drugs and other treatment modalities, the consent form is highly important to document and store. This field is required for the patient registration trigger event (C01). The time component is optional.
Definition: This field indicates whether the patient was an appropriate candidate for the trial. It is important for quality control and data analysis. The code set will vary among clinical trials. An example answer set is: Yes, No, By Approval, Not Assessed, Unknown. This field is required for the patient registration trigger event (C01). Refer to Table 0590 - Patient Study Eligibility Status in Chapter 2C for valid values.
Definition: This field contains the date the patient was randomized. The time component is optional. Up to three randomizations are supported. Sequential randomizations are listed in chronological order.
Definition: This field contains codes that must be developed by users. The blind treatment assignment may be communicated as a dummy text: ^blind or if a coded treatment assignment must also be communicated: 1^blind^local_code. If more than one randomization occurs, the second and third repetitions will correspond to the second and third repetitions of CSR-11 Study Randomization Date/Time, if they exist. Refer to Table 0591 - Randomized Study Arm in Chapter 2C for valid values.
Definition: Many studies have stratified randomization schemas. The strata codes must be developed for each clinical trial. This field is important for statistical analysis of the study results. The second and third repetitions will correspond to the second and third repetitions of CSR-11 Study Randomization Date/Time and CSR-12 Randomized Study Arm, if they exist. Refer to Table 0592 - Stratum for Study Randomization in Chapter 2C for valid values.
Definition: This field categorizes the inclusion of this patient's data for various analyses. The patient's data may be evaluable for analysis of adverse events but not for outcomes. Or it may be evaluable for some outcomes and not others. The coding systems will vary among trials. This field is required for the off-study trigger event (C04). Refer to Table 0593 - Patient Evaluability Status in Chapter 2C for valid values.
Definition: This field contains the date the patient completes or is otherwise removed from the study. This field is required for the off-study event (C04). The time component is optional.
Definition: This information is important for quality control and data analysis. The coding systems will vary among trials. An example answer set is: Adverse Events, Completed Trial, Death, Drug Resistance, Intercurrent Illness, Lost to Follow up, No Response to Therapy, Noncompliance, Progression of Disease, Protocol Violation, Refused Further Therapy. This field is required for the off-study trigger event (C04). Refer to Table 0594 - Reason Ended Study in Chapter 2C for valid values.
(Definition from OH1.2 in Ch. 3)
Definition: This field contains a code defining the action to be taken for this segment. It allows this segment to be sent to delete or update, for example, previously sent information. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 – Segment Action Code in Chapter 2C, Code Tables, for valid values.
(Definition from OH2.2 in Ch. 3)
Definition: This field contains a code defining the action to be taken for this segment. It allows this segment to be sent to delete or update, for example, previously sent information. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 – Segment Action Code in Chapter 2C, Code Tables, for valid values.
(Definition from OH3.2 in Ch. 3)
Definition: This field contains a code defining the action to be taken for this segment. It allows this segment to be sent to delete or update, for example, previously sent information. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 – Segment Action Code in Chapter 2C, Code Tables, for valid values.
(Definition from OH4.2 in Ch. 3)
Definition: This field contains a code defining the action to be taken for this segment. It allows this segment to be sent to delete or update, for example, previously sent information. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 – Segment Action Code in Chapter 2C, Code Tables, for valid values.
(Definition from ORC.35 in Ch. 4)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code for valid values.
The action code can only be used when either ORC-2 and/or ORC 3 is valued with a unique identifier in accordance with Chapter 2, Section 2.10.4.2.
(Definition from OBR.55 in Ch. 4)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code for valid values.
The action code can only be used when either an OBR-2 and/or OBR-3 is valued with unique identifier in accordance with Chapter 2, Section 2.10.4.2.
(Definition from IPC.10 in Ch. 4)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code for valid values.
The action code can only be used when the combination of IPC-1, IPC-2, IPC-3, and IPC-4 represents a unique identifier according to Chapter 2, Section 2.10.4.2.
(Definition from BPX.22 in Ch. 4)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code for valid values.
The action code can only be used when an BPX is uniquely identified sufficiently within the specific implementation using BPX-17 or BPX-6 as agreed to by the trading partners and in accordance with Chapter 2, Section 2.10.4.2.
(Definition from BTX.21 in Ch. 4)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code for valid values.
The action code can only be used when an BTX is uniquely identified sufficiently within the specific implementation using BTX-20 or BTX-3 as agreed to by the trading partners in accordance with Chapter 2, Section 2.10.4.2.
(Definition from DON.34 in Ch. 4)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code for valid values.
The action code can only be used when an DON is uniquely identified sufficiently within the specific implementation using DON-1 in accordance with Chapter 2, Section 2.10.4.2.
(Definition from BUI.13 in Ch. 4)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code for valid values.
The action code can only be used when an BUI is uniquely identified sufficiently within the specific implementation using BUI-2 in accordance with Chapter 2, Section 2.10.4.2
(Definition from RXV.22 in Ch. 4A)
Definition: The intended handling by the receiver of the infusion order is represented by this segment. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 – Segment Action Code in Chapter 2C, Code Tables, for valid values.
(Definition from CDO.2 in Ch. 4A)
Definition: The Action Code indicates whether the cumulative dosage segment is intended to be added, deleted, updated, or did not change. If the field is not valued in any CDO segments for the order, the segments are considered to have been sent in snapshot mode. If some but not all CDO segments for the order do not have the action code valued, the default value is Add. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code in Chapter 2C, Code Tables, for valid values.
(Definition from OBR.55 in Ch. 7)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code for valid values.
The action code can only be used when an either OBR-2 and/or OBR-3 is valued with unique identifier in accordance with Chapter 2, Section 2.10.4.2.
(Definition from OBX.31 in Ch. 7)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code for valid values.
The action code can only be used when an OBX-21 is valued in accordance with guidance in Chapter 2, Section 2.10.4.2.
(Definition from SPM.35 in Ch. 7)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code for valid values.
The action code can only be used when an SPM-2 or SPM-31 is valued in accordance with the guidance in Chapter 2, Section 2.10.4.2.
(Definition from PRT.2 in Ch. 7)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0287 – Problem/goal action code for valid values.
(Definition from CSR.17 in Ch. 7)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code for valid values.
The action code can only be used when CSR-1 and CSR-4, or CSR-2 and CSR-5 are valued as agreed to by the trading partners in accordance with the guidance in Chapter 2, Section 2.10.4.2.
(Definition from CTI.4 in Ch. 7)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code for valid values.
The action code can only be used when CTI-1 is valued in accordance with the guidance in Chapter 2, Section 2.10.4.2.
(Definition from SHP.12 in Ch. 7)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code for valid values.
The action code can only be used when SHP-1 is valued in accordance with the guidance in Chapter 2, Section 2.10.4.2.
(Definition from PAC.9 in Ch. 7)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0206 - Segment Action Code for valid values.
The action code can only be used when PAC-2 is valued in accordance with the guidance in Chapter 2, Section 2.10.4.2.
(Definition from GOL.1 in Ch. 12)
Definition: The action code field gives the intent of the problem or goal. Refer to HL7 Table 0287 – Problem/Goal Action Code in Chapter 2C, Code Tables, for valid values.
(Definition from PRB.1 in Ch. 12)
Definition: This field contains the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0287 – Problem/Goal Action Code in Chapter 2C, Code Tables, for valid values.
(Definition from PTH.1 in Ch. 12)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0287 – Problem/Goal Action Code in Chapter 2C, Code Tables, for valid values.
(Definition from DEV.1 in Ch. 17)
Definition: This field reveals the intent of the message. Refer to HL7 Table 0287 – Problem/goal action code for valid values.